Structure
of Flower
|
A.
Give
functions or definitions of the following parts of a flower: |
||
|
1.
|
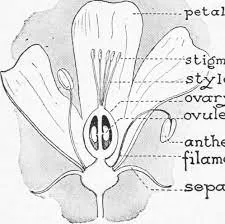
Stigma |
The stigma is the receptive surface,
where pollen grains land during pollination. |
|
2.
|
Ovary |
·
The
ovary contains ovules, which upon fertilization develop into seeds. ·
It
also matures into a fruit to protect the seeds and aid in their dispersal. |
|
3.
|
Petals |
Petals often have bright colors and
fragrances that attract pollinators like insects and birds, aiding in the
transfer of pollen from flower to flower. |
|
4.
|
Sepals |
Sepals are leaf-like structures at
the base of a flower that ·
protect
the bud before it blooms, ·
support
the petals when the flower is in bloom. ·
being
green, also perform photosynthesis for the plant. |
|
5.
|
Anther |
The anther produces and releases
pollen grains |
|
6.
|
Style |
·
Style
is the stalk-like structure that connects the stigma to the ovary. ·
It
also provides a pathway for pollen tubes to deliver male gametes to the
ovules for fertilization |
|
7.
|
Ovules |
The ovules contain the female
gametes (eggs) and upon fertilization develop into seeds |
|
8.
|
Filament |
The filament supports the anther
and positions it for pollen dispersal. |
|
9.
|
Pollen tube |
The pollen tube delivers the male
gametes (sperm cells) from the pollen grain to the ovule for fertilization. |
|
10. |
Receptacle |
The
receptacle is the swollen tip of the flower stalk (pedicel) where all floral
parts are attached |
|
11. |
Complete
flower |
A
complete flower possesses all four main floral parts: sepals, petals,
stamens, and pistils. |
|
12. |
Incomplete
flower |
An
incomplete flower lacks one or more of the main floral parts (sepals, petals,
stamens, pistils). |
|
13. |
Pollen |
Pollen
is a fine powder produced by the anther of a flower, containing the male
gametes (sperm cells). |
|
14. |
Pollination |
Pollination is the transfer of
pollen grains from the male reproductive organs (anthers) to the female
reproductive organs (stigma) of a flower. |
|
15. |
Fertilization |
Fertilization is the fusion of male
and female gametes (pollen and egg) leading to the formation of a zygote,
which develops into a seed. |
|
16. |
Germination |
Germination is the process by which
a seed sprouts and begins to grow into a new plant. It typically involves the
absorption of water, activation of enzymes, and emergence of the embryonic
plant from the seed coat. |
|
17. |
Seed dispersal |
Seed dispersal is the movement of
seeds away from the parent plant. It can be achieved through various
mechanisms such as wind, water, animals, or self-propulsion mechanisms in
some plants. |
|
18. |
Cross-pollination |
Cross-pollination
occurs when pollen from one flower is transferred to the stigma of a flower
on a different plant, promoting genetic diversity |
|
19. |
Self-pollination |
Self-pollination
occurs when pollen from the anther of a flower fertilizes the stigma of the
same flower or another flower on the same plant. |
|
20. |
Fruit |
Fruit
is the mature ovary of a flower, containing seeds and often serving as a
means of seed dispersal. |
|
21. |
Seed |
A
seed is a mature ovule containing an embryo, surrounded by a protective seed
coat, capable of developing into a new plant under suitable conditions. |
|
B.
Name
the following parts of a flower: |
||
|
1.
|
The male reproductive parts of a
flower |
Stamens |
|
2.
|
Female reproductive part of a
flower |
Pistil |
|
3.
|
Female gamete present in the ovule |
Egg or ovum |
|
4.
|
The two main parts of the stamen |
Anther & filament |
|
5.
|
The swollen part of the stalk where
all parts of the flower are attached |
Receptacle |
|
6.
|
The male gamete in a flower |
Pollen grain |
|
7.
|
Part
of a flower that protects the bud before it blooms |
Sepal |
|
8.
|
The
part of a flower where pollen is produced |
Anther |
|
9.
|
The
structure that connects the stigma to the ovary |
Style |
|
10. |
Part
of the flower receives pollen during pollination |
Stigma |
|
11. |
Thread-like
structure that connects the anther to the filament |
Filament |
|
12. |
The
part of the flower where fertilization occurs |
Ovule |
|
13. |
The
process of transferring pollen from the anther to the stigma |
Pollination |
|
14. |
The
female gamete found within the ovule |
Egg
cell |
|
15. |
The
outermost whorl of a flower, consisting of sepals |
Calyx |
|
16. |
The
structure that supports the stigma and style in a flower |
Ovary |
|
17. |
Part
of the flower that is responsible for attracting pollinators |
Petals |
|
18. |
The
female reproductive structure that contains the ovules |
Ovary |
7. How is self-pollination different
from cross-pollination?
Answer: Self-pollination occurs when pollen
is transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or a different
flower on the same plant, while cross-pollination involves the transfer of
pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a
different plant of the same species.
Comments